Waterfall flow
Age verification with k-ID is a privacy-preserving process that allows users to prove their age without revealing personal information. This approach uses a Waterfall flow model.
Waterfall flow
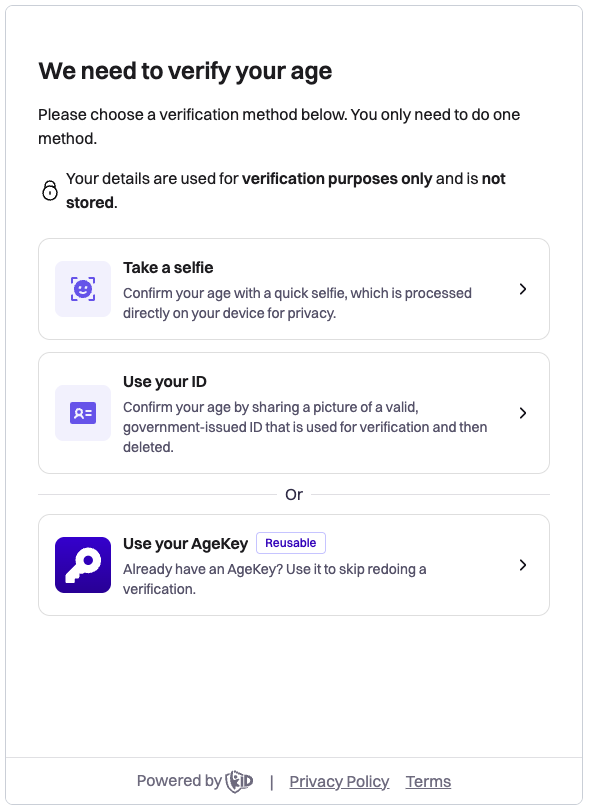
AgeKit+ acts as a single-point orchestrator for age checks, automatically cascading through a waterfall of verification providers to confirm a user's age. In practice, one API call to k-ID presents the configured methods in sequence. For example, starting with email inference or a facial age estimation and then falling back to an ID document scan or other methods as needed, until the user's age is verified or all options are exhausted. This means developers integrate once with k-ID's API, and the platform handles trying multiple verification techniques behind the scenes, combining methods to maximize the chances of a successful verification.
The verification flow is initiated with an API call that returns a URL to be hosted in an iframe or mobile web view, where users complete the verification process. The available verification methods are determined by your product configuration in the Compliance Studio, ensuring compliance with jurisdiction requirements.
| API | Scenario |
|---|---|
/age-verification/perform-access-age-verification | To verify the age of a user before getting access to a feature, mature content, or the product itself. |
/age-verification/perform-trusted-adult-verification | To perform trusted adult (parent or guardian) verification. |
/age-verification/perform-age-appeal | For users who have failed age verification but want to appeal the decision. |
The Age Verification APIs are standardized in terms of the request & response format.
Request body
| Property | Description | Required? |
|---|---|---|
jurisdiction | The jurisdiction in which the age verification should happen | Yes |
criteria | The criteria for age verification | Yes |
subject.email | If the user verified their age with k-ID in any other context with an email address, then the original age is returned instead of asking the user to estimate or prove their age again. | No |
subject.claimedAge | If a user was asked for their age in an age gate, used to inform the age estimation process | No |
subject.id | An identifier used across multiple verification methods to report multiple failed attempts. This can be a temporary session ID, or hashed user ID. | No |
options.facialAgeEstimation.passIfOver | The estimated age threshold required to automatically pass facial age estimation. If the estimated age is at or greater than this value, the verification passes. | No |
options.facialAgeEstimation.failIfUnder | The estimated age threshold below which the verification fails. If the estimated age is below this value, the verification fails. Defaults to the verification criteria age when omitted. | No |
options.redirectUrl | The URL to redirect to after verification completes. Supports HTTP/HTTPS URLs or mobile deeplinks with custom protocol schemes. The redirect only occurs when the verification URL is opened directly in a browser or webview (not embedded in an iframe). When a redirect occurs, the URL includes verificationId and result (PASS or FAIL) as query string parameters. | No |
The passIfOver and failIfUnder parameters give you control over the variance allowed in facial age estimation results. When a facial age estimation scan is performed:
- If the estimated age is at or greater than
passIfOver, the verification PASSES and an age signal is determined. - If the estimated age is below
failIfUnder, the verification FAILS and an age signal is determined. - If the estimated age is greater than
failIfUnderand less thanpassIfOver, the result is considered inconclusive and the user can retry the facial age estimation.
This allows you to set a confidence range where results are clear enough to make a determination, while giving users the opportunity to retry when the estimation falls in an uncertain range. For example, if you need to verify users are 18+, you might set passIfOver to 25 and failIfUnder to 12. This means users estimated to be 25 or older pass immediately, users estimated to be below 12 fail immediately, and users estimated to be 12-24 can retry the scan or other verification methods.
Sample:
{
"jurisdiction": "US-CA",
"criteria": {
"ageCategory": "ADULT"
},
"options": {
"facialAgeEstimation": {
"passIfOver": 25,
"failIfUnder": 12
},
"redirectUrl": "https://example.com/verification-complete"
}
}
Redirect URL
The redirectUrl parameter allows you to specify where users should be redirected after completing verification. This is useful for:
- Browser-based flows: Redirecting to another web page after verification completes
- Custom success screens: Displaying your own custom success or failure page
- Mobile app deeplinks: Using custom protocol schemes (for example,
myapp://verification-complete) to return control to your mobile app
The redirect only occurs when the verification URL is opened directly in a browser or webview (not embedded in an iframe). When embedded in an iframe, verification results are delivered via DOM events instead.
When a redirect occurs, the redirect URL includes the following query string parameters:
verificationId: The unique verification IDresult: The verification result, eitherPASSorFAIL
Example redirect URL:
https://example.com/verification-complete?verificationId=7854909b-9124-4bed-9282-24b44c4a3c97&result=PASS
Response body
A successful request to the Age Verification API returns the following response.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
id | A unique verification ID generated by Age Verification Service |
url | The age verification URL that must be embedded in an iframe and presented to the user, for them to verify themselves. |
Sample:
{
"id": "7854909b-9124-4bed-9282-24b44c4a3c97",
"url": "https://family.k-id.com/verify?token=eyJ..."
}
Verification URL validity
The verification URL is valid for 2 weeks after creation. The expiry is encoded in the JWT in the URL's token query parameter. To determine whether a previously generated URL is still valid without opening it, decode the JWT and inspect the standard exp claim, which contains the expiration time.
If a user returns after the URL has expired, use the saved verification ID to call /age-verification/get-status. If the verification no longer exists (for example, it was never completed and has been removed), create a new verification by calling the perform endpoint again.
Embedding the verification interface
Use the returned URL to create an iframe in your website or app. Users complete their verification through this interface, with available methods automatically adapting to jurisdictional requirements.
<div id="verification-container">
<iframe
id="verification-widget"
src="VERIFICATION_URL"
width="100%"
height="600"
frameborder="0"
allow="camera;payment;publickey-credentials-get;publickey-credentials-create">
</iframe>
</div>
The allow attribute is required to enable the following features:
camera: Required for facial age estimationpayment: Required for credit card verificationpublickey-credentials-getandpublickey-credentials-create: Required for WebAuthn-based verification methods
Verification result
Once the user has successfully completed the age verification, or the user has retried the maximum number of times and hasn't succeeded, the Age Verification Result is delivered through both client-side and server-side channels. Implementations should use a combination of both: client-side events are best for controlling UI elements, while for data integrity, the actual results should come from either a webhook or a call to /age-verification/get-status.
For detailed information about analyzing verification results, including field presence rules, status types, and implementation guidance, see the Verification Event Contract.
Client-side (DOM events) - If the URL from the response body is included in an iframe, it's sent to the parent frame as a window message (MessageEvent) with a Verification.Result structure.
Server-side (webhooks) - An event is sent to the registered webhook in the form of a Verification.Result event.
Example of accessing the window message:
const handleMessage = (event: MessageEvent) => {
const message = event.data;
if (message.eventType === "Verification.Result") {
// Use DOM Events for immediate UI updates
updateUI(message);
}
};
window.addEventListener("message", handleMessage);
For data integrity, always verify results with events from webhooks or by calling /age-verification/get-status rather than relying solely on DOM Events. DOM Events are best suited for responsive UI updates.
The data element of the window event and the webhook event contains the following properties.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
id | The verification ID for which this is the result. |
status | Indicates a PASS or FAIL status, based on whether the user met the age criteria or not. |
ageCategory | Indicates the age category the user belongs to in the jurisdiction specified in the request. Supported values are adult, digital-youth or digital-minor |
method | Indicates the method used for the verification. Supported values are id-document, age-estimation, age-attestation, credit-card, social-security-number |
failureReason | The reason the verification failed. Supported values are age-criteria-not-met, max-attempts-exceeded, or fraudulent-activity-detected. This is only set if status is FAIL |
age | Returns the lower bound and higher bound of the estimated or verified age as low and high. |
Sample:
{
"eventType": "Verification.Result",
"data": {
"id": "5a58e98a-e477-484b-b36a-3857ea9daaba",
"status": "PASS",
"ageCategory": "adult",
"method": "id-document",
"age": {
"low": 25,
"high": 25,
}
}
}
Handling a window event:
const handleMessage = (event: MessageEvent) => {
const message = event.data;
if (message.eventType === "Verification.Result") {
if (message.data.status === "PASS") {
window.location.href = `https://www.example.com/success?verificationId=${message.data.id}`
}
if (message.data.status === "FAIL") {
window.location.href = `https://www.example.com/fail?verificationId=${message.data.id}`
}
}
};
window.addEventListener("message", handleMessage);
Verification error
If an unexpected error has occurred, a JavaScript event fires so that your implementation can gracefully handle the error.
For detailed information about the event structure, see Verification.Error.
Sample Message:
{
"eventType": "Verification.Error",
"method": "credit-card",
"status": "ERROR"
}
Checking verification status
You can get the status of a verification independent of the verification URL by calling /age-verification/get-status with the verification ID. This is useful when:
- The registered webhook was unreachable and the status event was never received
- You need to check status without redirecting the user to the verification URL
- A previously generated URL has expired and you want to see if the verification was already completed
The data structure returned follows the same contract as the Verification.Result webhook event, but there are some differences in structure and field presence. For detailed information about analyzing verification results, including field presence rules, status types, differences between webhook and API endpoint responses, and implementation guidance, see the Verification Event Contract. For more information about webhook events, see Webhooks.
Handling expired verification URLs
If a user has an expired verification URL (valid for 2 weeks after creation):
- Call
/age-verification/get-statuswith the saved verification ID. - If the verification exists, use the returned status (for example,
PASSorFAIL). - If get-status returns 400 with error code
INVALID_INPUT, create a new verification by calling the perform endpoint again and present the new URL to the user.
Verification retention
Verifications that remain in PENDING status for more than 2 weeks are deleted from the system. After deletion, /age-verification/get-status returns 400 with error code INVALID_INPUT; callers should treat that response as requiring a new verification to be created.
Edge case handling
When processing verification results, you must handle variations in the response structure depending on the verification outcome and failure reason. The following examples demonstrate correct and incorrect handling patterns for different response variations. For complete field presence rules, see the Verification Event Contract.
Partial attempt (max attempts exceeded)
When a user exhausts all verification attempts without a conclusive age determination, the verification fails with max-attempts-exceeded. This response doesn't include method, age, or ageCategory fields.
Example payload:
{
"eventType": "Verification.Result",
"data": {
"id": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174002",
"status": "FAIL",
"failureReason": "max-attempts-exceeded"
}
}
Example payload for age-criteria-not-met (for comparison):
{
"eventType": "Verification.Result",
"data": {
"id": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174001",
"status": "FAIL",
"method": "age-estimation-scan",
"failureReason": "age-criteria-not-met",
"age": {
"low": 16,
"high": 17
}
}
}
Incorrect handling:
// ❌ WRONG: Assumes method and age are always present for FAIL
const handleVerification = (result: VerificationResult) => {
if (result.data.status === "FAIL") {
// These fields are undefined when failureReason is max-attempts-exceeded
logFailedMethod(result.data.method);
recordFailedAge(result.data.age.low);
showRetryWithMethod(result.data.method);
}
};
Correct handling:
// ✅ CORRECT: Handles different failure scenarios appropriately
const handleVerification = (result: VerificationResult) => {
if (result.data.status === "FAIL") {
denyAccess();
switch (result.data.failureReason) {
case "max-attempts-exceeded":
// No age determination was made - offer alternative options
showMaxAttemptsMessage();
offerSupportContact();
// Consider implementing rate limiting for future attempts
break;
case "age-criteria-not-met":
// Age was determined but didn't meet criteria
// method and age fields are available
if (result.data.age) {
logDeterminedAge(result.data.age.low);
}
showAgeCriteriaNotMetMessage();
break;
case "fraudulent-activity-detected":
// Handle suspicious activity (see next section)
handleSuspiciousActivity(result.data.id);
break;
default:
// Handle unknown failure reasons gracefully
logUnknownFailure(result.data.failureReason);
showGenericFailureMessage();
}
}
};
Suspicious activity detected
When the system detects potentially fraudulent behavior, the verification fails with fraudulent-activity-detected. This response excludes age data and doesn't include the method field.
Example payload:
{
"eventType": "Verification.Result",
"data": {
"id": "123e4567-e89b-12d3-a456-426614174003",
"status": "FAIL",
"failureReason": "fraudulent-activity-detected"
}
}
Incorrect handling:
// ❌ WRONG: Treats fraudulent activity like a normal failure
const handleVerification = (result: VerificationResult) => {
if (result.data.status === "FAIL") {
// Allowing immediate retry could enable continued abuse
showRetryButton();
// Logging age data that doesn't exist
analytics.track("verification_failed", {
age: result.data.age?.low // undefined for fraudulent activity
});
}
};
Correct handling:
// ✅ CORRECT: Implements appropriate security measures
const handleVerification = (result: VerificationResult) => {
if (result.data.status === "FAIL") {
denyAccess();
if (result.data.failureReason === "fraudulent-activity-detected") {
// Log the security event for review
securityLog.warn("Fraudulent activity detected", {
verificationId: result.data.id,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
subjectId: currentSubjectId
});
// Implement stricter rate limiting or temporary blocks
applySecurityCooldown(currentSubjectId);
// Show appropriate message without revealing detection details
showVerificationUnavailableMessage();
// Don't offer immediate retry - this could enable continued abuse
hideRetryOptions();
// Optionally flag for manual review
flagForManualReview(result.data.id);
}
}
};
Complete edge case handler
The following example shows a comprehensive handler that correctly processes all edge cases:
interface VerificationData {
id: string;
status: "PASS" | "FAIL";
method?: string;
ageCategory?: "adult" | "digital-youth" | "digital-minor"; // Always present for PASS status
age?: { low: number; high: number }; // Always present for PASS status
dob?: string;
failureReason?: string;
}
const handleVerificationResult = (data: VerificationData) => {
// Always log the verification attempt
logVerificationAttempt(data.id, data.status);
if (data.status === "PASS") {
// Grant access - the user met the age criteria
grantAccess();
// age and ageCategory are always present for PASS status
storeAgeData(data.age.low, data.age.high);
applyPermissionsForCategory(data.ageCategory);
// Process optional fields only if present
if (data.dob) {
storeDateOfBirth(data.dob);
}
if (data.method) {
analytics.track("verification_passed", { method: data.method });
}
return;
}
// Handle FAIL status
denyAccess();
// failureReason is always present for FAIL status
switch (data.failureReason) {
case "age-criteria-not-met":
// method and age are available for this failure reason
handleAgeCriteriaFailure(data);
break;
case "max-attempts-exceeded":
// No age determination - method and age are NOT available
handleMaxAttemptsFailure(data.id);
break;
case "fraudulent-activity-detected":
// Security event - method and age are NOT available
handleFraudulentActivity(data.id);
break;
default:
// Always handle unknown failure reasons gracefully
handleUnknownFailure(data);
}
};
Always check for field presence before accessing optional fields. The Verification Event Contract provides complete field presence rules for each status and failure reason combination.
Limiting verification attempts
Each verification request allows users three attempts per available verification method. A verification fails if:
- All available verification methods have been exhausted and an age can't be determined
- An age is determined but falls below the required threshold for your criteria
When a verification fails, you can allow users to initiate a new verification attempt. However, to prevent misuse and abuse of the verification system, you should implement rate limiting on additional verification attempts. For example, you might limit users to three verification attempts within a 24-hour period.
Use the subject.id field in the verification request to track attempts across multiple verification requests. This field should contain a consistent identifier for the user (such as a temporary session ID or hashed user ID), allowing you to:
- Track the number of verification attempts per user
- Implement time-based rate limiting (for example, 3 attempts per 24 hours)
- Prevent users from bypassing limits by creating new sessions
Implement rate limiting on your server before initiating verification requests. This prevents unnecessary API calls and helps protect your system from abuse.
Verification methods
For detailed information about all available verification methods, see Verification methods.